Development Basics with Vanilla JS
Now that you've setup your project, it's time to give it a test run in the browser.
If you haven't started Vite in the terminal, do so now:
npm run dev
Install the extension
When the build completes, open Chrome or Edge and navigate to
chrome://extensions. Make sure to turn on the developer mode switch.
| Chrome | Edge |
|---|---|
| Located in top right corner | Located in left sidebar |
Drag your dist folder into the Extensions Dashboard to install it. Your
extension icon will be in the top bar. The icon will be the first letter of the
extension's name.
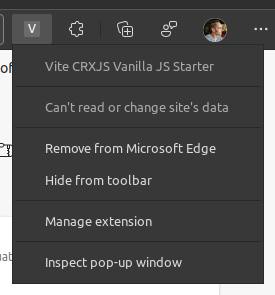
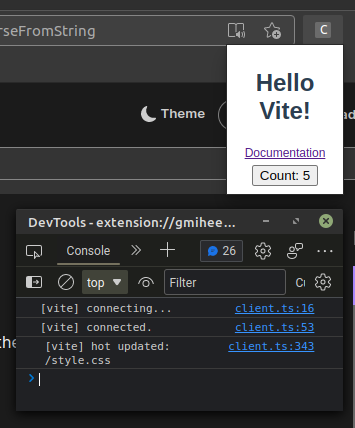
Inspect the popup
Once you've found the extension icon, right-click it and choose "Inspect popup window". This menu item will open the popup and the popup dev tools window. We need to inspect the popup to keep it open while making changes.
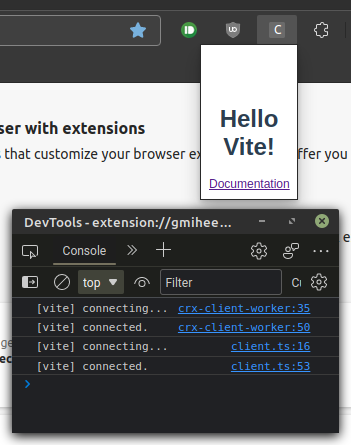
Vite HMR for JavaScript
Let's see how Vite handles JavaScript updates without an HMR framework. We can add a counter button to test how Vite preserves the page state.
import './style.css'
document.querySelector('#app').innerHTML = `
<h1>Hello Vite!</h1>
<a href="https://vitejs.dev/guide/features.html" target="_blank">Documentation</a>
<button>Count: 0</button>
`
let count = 0
const button = document.querySelector('#app button')
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
count++
button.textContent = `Count: ${count}`
})
Vite will trigger a full page reload when we save our file. The popup will stay open since the devtools inspector is open. Our button is there, but the elements look a little squashed.
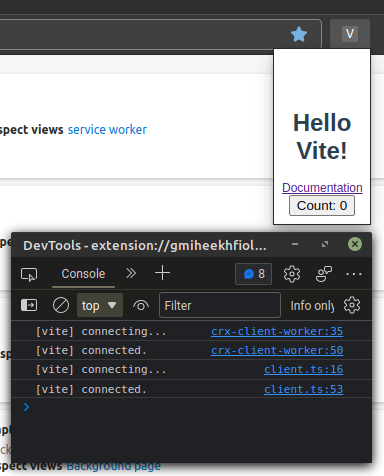
Vite HMR for CSS
HTML and JS changes trigger full page reloads, but Vite provides HMR updates for
imported styles without a full page reload. Click that counter a few times and
then update styles.css to fix the page layout.
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px; /* Remove this line */
width: 100px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
row-gap: 5px;
}
Vite will update the styles while preserving the counter state. Pretty good for a vanilla JavaScript project!